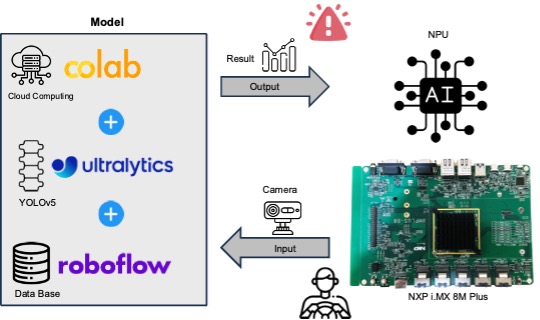
Overview
In today’s era of the full rise of artificial intelligence, the field of computer vision has undergone an epoch-making change. In the past, we relied on pixel-by-pixel processing technology to analyze images, but now, all of this has been replaced by deep learning driven by big data. This method uses huge data sets to train the so-called “model” to achieve more accurate and efficient image recognition. In this wave, the emergence of technologies such as generative AI and ChatGPT has subverted our imagination of artificial intelligence. Intelligent devices are no longer an unattainable dream, but a reality within reach. In particular, with the NXP i.MX8M Plus platform, edge computing combined with the object recognition YOLO algorithm is more efficient and popular.
YOLO Technology
YOLO (You Only Look Once) technology came into being. It is a revolutionary object detection technology that can simultaneously identify multiple objects in a single scan of an image, greatly improving processing speed and accuracy. YOLO has a wide range of application scenarios, from autonomous driving to security monitoring systems. In the past, scholars and engineers spent countless efforts to develop complex systems, but now with the support of the ultralytics community, it can be easily implemented through some simple steps.
Development Environment Construction
The first step in developing a platform is to establish the development environment for NXP embedded systems. Readers who do not understand this technology can read Getting Start to quickly deploy the K1 development environment.
Construction of a Drowsy Driving Monitoring System (DMS)
This article will use Google’s Colab cloud computing as a training platform, and use ultralytics’ YOLOv5 framework and the database provided by Roboflow to quickly build a Drowsy Driving Monitoring System (DMS) to monitor whether the driver is drowsy, and use K1 as the final hardware presentation platform.
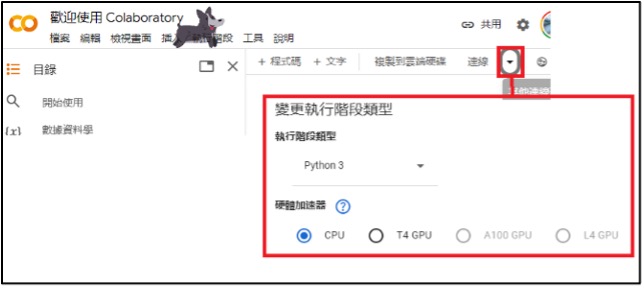
1、Open the Colab cloud computing platform and select GPU as the processing core.
2、Download the ultralytics code (YOLOv5 framework).
!git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov53、Install necessary packages.
%cd yolov5
%pip install -qr requirements.txt # install dependencies
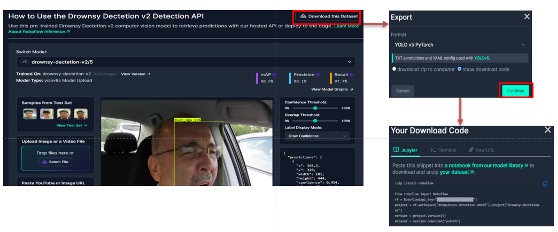
%pip install -q roboflow4、Install Roboflow. Roboflow is an online data management platform that has functions such as labeling image data, data enhancement, etc.
!pip install roboflow5、Download DataBase.
from roboflow import Roboflow
rf = Roboflow(api_key="********")
project = rf.workspace("drowsiness-detection-uhhz5").project("drownsy-dectetion-v2")
version = project.version(5)
dataset = version.download("yolov5pytorch")For this step, please go to the dronesy-dectetion-v2 on the roboflow website and follow the steps below to get the corresponding API Key.
6、Train AI models. !python train.py --img 256 --batch 16 --epochs 20 --data {dataset.location}/data.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --cache
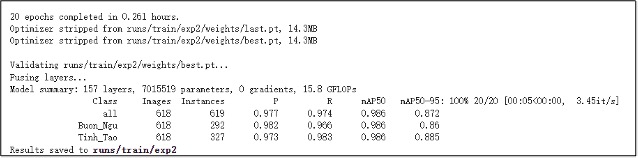
7、Validate AI models.
!python detect.py --weights /content/yolov5/runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt \
--img 256 --conf 0.1 --source {dataset.location}/test/images
Note : 请到 /content/yolov5/runs/detect View the test results.
8、Export AI model Convert the Pytorch module to Tensorflow Lite format.
!python export.py --weights /content/yolov5/runs/train/exp/weights/best.pt --img-size 256 --include tflit
9、Output AI Model (Quantized Integer Version) Convert Tensorflow to Tensorflow Lite module and quantize weights to integer form.
# Tensorflow to TF Lite (INT)
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def representative_dataset_gen(): # Simulated Dataset (Randomized Test Set Image Accuracy)
for _ in range(250):
yield [np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0 , size=(1,256,256,3)).astype(np.float32)]
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model("/content/yolov5/runs/train/exp/weights/best_saved_model")
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
converter.target_spec.supported_ops = [tf.lite.OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8]
converter.allow_custom_ops = True
converter.inference_input_type = tf.float32
converter.inference_output_type = tf.float32
converter.representative_dataset = representative_dataset_gen
tflite_model = converter.convert()
with tf.io.gfile.GFile("DrownsyDectetion_v2-quant.tflite", 'wb') as f:
f.write(tflite_model)
print("Quantization complete! - model.tflite")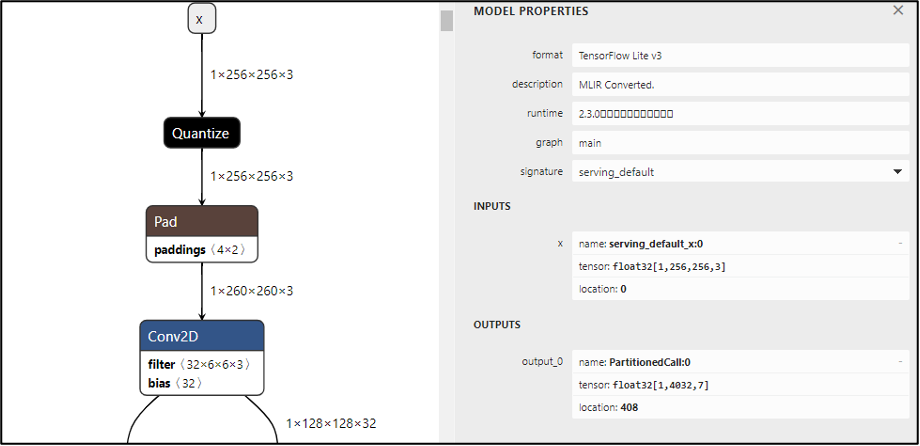
Run on K1 platform
Finally, you only need to deploy the module to K1 to realize the terminal edge computing application “Driving Fatigue Monitoring System (DMS)”! Please operate the following code in the system of K1 platform.
Note: You can quickly get this case code on bit-brick’github
- Create a project directory
mkdir YOLOv5s_DrownsyDection_v2
cd YOLOv5s_DrownsyDection_v2
mkdir model img output- Copy the test images and model files
cp DrownsyDection_v2-quant.tflite /home/root/YOLOv5s_DrownsyDection_v2/model
cp test.jpg /home/root/YOLOv5s_DrownsyDection_v2/img- Create plot.py and app.py scripts plot.py contains auxiliary functions for plotting prediction results. app.py is the main script of the application, containing the logic of model loading, inference, and result display.
plot.py
import cv2
import torch
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
FONT = 'Arial.ttf'
class Colors:
# Ultralytics color palette https://ultralytics.com/
def __init__(self):
# hex = matplotlib.colors.TABLEAU_COLORS.values()
hexs = ('FF3838', 'FF9D97', 'FF701F', 'FFB21D', 'CFD231', '48F90A', '92CC17', '3DDB86', '1A9334', '00D4BB',
'2C99A8', '00C2FF', '344593', '6473FF', '0018EC', '8438FF', '520085', 'CB38FF', 'FF95C8', 'FF37C7')
self.palette = [self.hex2rgb(f'#{c}') for c in hexs]
self.n = len(self.palette)
def __call__(self, i, bgr=False):
c = self.palette[int(i) % self.n]
return (c[2], c[1], c[0]) if bgr else c
@staticmethod
def hex2rgb(h): # rgb order (PIL)
return tuple(int(h[1 + i:1 + i + 2], 16) for i in (0, 2, 4))
colors = Colors() # create instance for 'from utils.plots import colors'
def check_pil_font(font=FONT, size=10):
# Return a PIL TrueType Font, downloading to CONFIG_DIR if necessary
font = Path(font)
font = font if font.exists() else (CONFIG_DIR / font.name)
try:
return ImageFont.truetype(str(font) if font.exists() else font.name, size)
except Exception: # download if missing
try:
check_font(font)
return ImageFont.truetype(str(font), size)
except TypeError:
check_requirements('Pillow>=8.4.0') # known issue https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/5374
except URLError: # not online
return ImageFont.load_default()
def is_ascii(s=''):
# Is string composed of all ASCII (no UTF) characters? (note str().isascii() introduced in python 3.7)
s = str(s) # convert list, tuple, None, etc. to str
return len(s.encode().decode('ascii', 'ignore')) == len(s)
class Annotator:
# YOLOv5 Annotator for train/val mosaics and jpgs and detect/hub inference annotations
def __init__(self, im, line_width=None, font_size=None, font='Arial.ttf', pil=False, example='abc'):
assert im.data.contiguous, 'Image not contiguous. Apply np.ascontiguousarray(im) to Annotator() input images.'
non_ascii = not is_ascii(example) # non-latin labels, i.e. asian, arabic, cyrillic
self.pil = pil or non_ascii
if self.pil: # use PIL
self.im = im if isinstance(im, Image.Image) else Image.fromarray(im)
self.draw = ImageDraw.Draw(self.im)
self.font = check_pil_font(font='Arial.Unicode.ttf' if non_ascii else font,
size=font_size or max(round(sum(self.im.size) / 2 * 0.035), 12))
else: # use cv2
self.im = im
self.lw = line_width or max(round(sum(im.shape) / 2 * 0.003), 2) # line width
def box_label(self, box, label='', color=(128, 128, 128), txt_color=(255, 255, 255)):
# Add one xyxy box to image with label
if self.pil or not is_ascii(label):
self.draw.rectangle(box, width=self.lw, outline=color) # box
if label:
w, h = self.font.getsize(label) # text width, height (WARNING: deprecated) in 9.2.0
# _, _, w, h = self.font.getbbox(label) # text width, height (New)
outside = box[1] - h >= 0 # label fits outside box
self.draw.rectangle(
(box[0], box[1] - h if outside else box[1], box[0] + w + 1,
box[1] + 1 if outside else box[1] + h + 1),
fill=color,
)
# self.draw.text((box[0], box[1]), label, fill=txt_color, font=self.font, anchor='ls') # for PIL>8.0
self.draw.text((box[0], box[1] - h if outside else box[1]), label, fill=txt_color, font=self.font)
else: # cv2
p1, p2 = (int(box[0]), int(box[1])), (int(box[2]), int(box[3]))
cv2.rectangle(self.im, p1, p2, color, thickness=self.lw, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(self.lw - 1, 1) # font thickness
w, h = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=self.lw / 3, thickness=tf)[0] # text width, height
outside = p1[1] - h >= 3
p2 = p1[0] + w, p1[1] - h - 3 if outside else p1[1] + h + 3
cv2.rectangle(self.im, p1, p2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(self.im,
label, (p1[0], p1[1] - 2 if outside else p1[1] + h + 2),
0,
self.lw / 3,
txt_color,
thickness=tf,
lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
def masks(self, masks, colors, im_gpu, alpha=0.5, retina_masks=False):
"""Plot masks at once.
Args:
masks (tensor): predicted masks on cuda, shape: [n, h, w]
colors (List[List[Int]]): colors for predicted masks, [[r, g, b] * n]
im_gpu (tensor): img is in cuda, shape: [3, h, w], range: [0, 1]
alpha (float): mask transparency: 0.0 fully transparent, 1.0 opaque
"""
if self.pil:
# convert to numpy first
self.im = np.asarray(self.im).copy()
if len(masks) == 0:
self.im[:] = im_gpu.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous().cpu().numpy() * 255
colors = torch.tensor(colors, device=im_gpu.device, dtype=torch.float32) / 255.0
colors = colors[:, None, None] # shape(n,1,1,3)
masks = masks.unsqueeze(3) # shape(n,h,w,1)
masks_color = masks * (colors * alpha) # shape(n,h,w,3)
inv_alph_masks = (1 - masks * alpha).cumprod(0) # shape(n,h,w,1)
mcs = (masks_color * inv_alph_masks).sum(0) * 2 # mask color summand shape(n,h,w,3)
im_gpu = im_gpu.flip(dims=[0]) # flip channel
im_gpu = im_gpu.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # shape(h,w,3)
im_gpu = im_gpu * inv_alph_masks[-1] + mcs
im_mask = (im_gpu * 255).byte().cpu().numpy()
self.im[:] = im_mask if retina_masks else scale_image(im_gpu.shape, im_mask, self.im.shape)
if self.pil:
# convert im back to PIL and update draw
self.fromarray(self.im)
def rectangle(self, xy, fill=None, outline=None, width=1):
# Add rectangle to image (PIL-only)
self.draw.rectangle(xy, fill, outline, width)
def text(self, xy, text, txt_color=(255, 255, 255), anchor='top'):
# Add text to image (PIL-only)
if anchor == 'bottom': # start y from font bottom
w, h = self.font.getsize(text) # text width, height
xy[1] += 1 - h
self.draw.text(xy, text, fill=txt_color, font=self.font)
def fromarray(self, im):
# Update self.im from a numpy array
self.im = im if isinstance(im, Image.Image) else Image.fromarray(im)
self.draw = ImageDraw.Draw(self.im)
def result(self):
# Return annotated image as array
return np.asarray(self.im)
app.py
# WPI Confidential Proprietary
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Copyright (c) 2021 Freescale Semiconductor
# Copyright 2021 WPI
# All Rights Reserved
##--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# * Code Ver : 2.0
# * Code Date: 2023/04/26
# * Author : Weilly Li
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY WPI-TW "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESSED OR
# IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
# OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED.
# IN NO EVENT SHALL WPI OR ITS CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT,
# INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
# (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
# SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION)
# HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT,
# STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING
# IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF
# THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# References:
# https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
#
import sys
import cv2
import torch
import torchvision
import time
import argparse
import numpy as np
import tflite_runtime.interpreter as tflite
from plots import Annotator, colors
# V4L2_YUV2_720p = "v4l2src device=/dev/video2 ! video/x-raw,format=YUY2,width=1280,height=720, pixel-aspect-ratio=1/1, framerate=30/1! videoscale!videoconvert ! appsink"
V4L2_YUV2_720p = "/dev/video5"
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# API
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def InferenceDelegate( model, delegate ):
if (delegate=="vx") :
interpreter = tflite.Interpreter(model, experimental_delegates=[ tflite.load_delegate("/usr/lib/libvx_delegate.so") ])
elif(delegate=="ethosu"):
interpreter = tflite.Interpreter(model, experimental_delegates=[tflite.load_delegate("/usr/lib/libethosu_delegate.so")])
elif(delegate=="xnnpack"):
interpreter = tflite.Interpreter(model)
else :
print("ERROR : Deleget Input Fault")
return 0
return interpreter
def Label_name(x):
names = {0:'drowsy', 1:'normal'}
return names[x]
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)
y[..., 0] = x[..., 0] - x[..., 2] / 2 # top left x
y[..., 1] = x[..., 1] - x[..., 3] / 2 # top left y
y[..., 2] = x[..., 0] + x[..., 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[..., 3] = x[..., 1] + x[..., 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def non_max_suppression(
prediction,
conf_thres=0.25,
iou_thres=0.45,
classes=None,
agnostic=False,
multi_label=False,
labels=(),
max_det=300,
nm=0, # number of masks
):
"""Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results to reject overlapping detections
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls]
"""
# Checks
assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
if isinstance(prediction, (list, tuple)): # YOLOv5 model in validation model, output = (inference_out, loss_out)
prediction = prediction[0] # select only inference output
device = prediction.device
mps = 'mps' in device.type # Apple MPS
if mps: # MPS not fully supported yet, convert tensors to CPU before NMS
prediction = prediction.cpu()
bs = prediction.shape[0] # batch size
nc = prediction.shape[2] - nm - 5 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Settings
# min_wh = 2 # (pixels) minimum box width and height
max_wh = 7680 # (pixels) maximum box width and height
max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()
time_limit = 0.5 + 0.05 * bs # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
t = time.time()
mi = 5 + nc # mask start index
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6 + nm), device=prediction.device)] * bs
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
lb = labels[xi]
v = torch.zeros((len(lb), nc + nm + 5), device=x.device)
v[:, :4] = lb[:, 1:5] # box
v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
v[range(len(lb)), lb[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
x = torch.cat((x, v), 0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box/Mask
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4]) # center_x, center_y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
mask = x[:, mi:] # zero columns if no masks
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:mi] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, 5 + j, None], j[:, None].float(), mask[i]), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = x[:, 5:mi].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float(), mask), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not torch.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[torch.isfinite(x).all(1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence and remove excess boxes
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
i = i[:max_det] # limit detections
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
if mps:
output[xi] = output[xi].to(device)
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
#LOGGER.warning(f'WARNING ⚠️ NMS time limit {time_limit:.3f}s exceeded')
break # time limit exceeded
return output
def clip_boxes(boxes, shape):
# Clip boxes (xyxy) to image shape (height, width)
if isinstance(boxes, torch.Tensor): # faster individually
boxes[..., 0].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x1
boxes[..., 1].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y1
boxes[..., 2].clamp_(0, shape[1]) # x2
boxes[..., 3].clamp_(0, shape[0]) # y2
else: # np.array (faster grouped)
boxes[..., [0, 2]] = boxes[..., [0, 2]].clip(0, shape[1]) # x1, x2
boxes[..., [1, 3]] = boxes[..., [1, 3]].clip(0, shape[0]) # y1, y2
def scale_boxes(img1_shape, boxes, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
# Rescale boxes (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
boxes[..., [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
boxes[..., [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
boxes[..., :4] /= gain
clip_boxes(boxes, img0_shape)
return boxes
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, stride=32):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better val mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 主程式
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def main():
# 解析外部資訊
APP_NAME = "YOLOv5s_DrownsyDectetion_v2"
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument( '-c' ,"--camera", default="0")
parser.add_argument( '-d' ,"--display", default="0")
parser.add_argument("--save", default="1")
parser.add_argument( '-t', "--time", default="0")
parser.add_argument('--delegate' , default="vx", help = 'Please Input vx or xnnpack or ethosu')
parser.add_argument( '-m', '--model' , default="model/DrownsyDectetion_v2-quant.tflite", help='File path of .tflite file.')
parser.add_argument("--test_img", default="img/test2.jpg")
args = parser.parse_args()
# 解析解譯器資訊
interpreter = InferenceDelegate(args.model,args.delegate)
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
input_details = interpreter.get_input_details()
output_details = interpreter.get_output_details()
width = input_details[0]['shape'][2]
height = input_details[0]['shape'][1]
nChannel = input_details[0]['shape'][3]
scale, zero_point = input_details[0]['quantization']
#print(scale)
# 先行進行暖開機
if (input_details[0]['dtype']==np.uint8) :
interpreter.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], np.zeros((1,height,width,nChannel)).astype("uint8") )
else :
interpreter.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], np.zeros((1,height,width,nChannel)).astype("float32") )
interpreter.invoke()
last_frame_time = time.time()
# 是否啟用攝鏡頭
if args.camera =="True" or args.camera == "1" :
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(V4L2_YUV2_720p)
if(cap.isOpened()==False) :
print( "Open Camera Failure !!")
sys.exit()
else :
print( "Open Camera Success !!")
# 迴圈 / 重複推理
while(True):
# 視訊/影像資料來源
if args.camera =="True" or args.camera == "1" :
ret, frame = cap.read()
else :
frame = cv2.imread(args.test_img)
frame_resized = letterbox(frame, (width,height), stride=32, auto=False)[0] # padded resize
#frame_resized = cv2.cvtColor(frame_resized, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
#frame_resized = cv2.cvtColor(frame_resized, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB)
frame_resized = frame_resized.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
frame_resized = np.ascontiguousarray(frame_resized)
if (input_details[0]['dtype']==np.uint8) :
frame_resized = (frame_resized/scale) + zero_point
else :
frame_resized = (frame_resized/255.0)
# 設置來源資料至解譯器
if (input_details[0]['dtype']==np.uint8) :
input_data = np.expand_dims(frame_resized , axis=0).astype(np.uint8)
else :
input_data = np.expand_dims(frame_resized , axis=0).astype(np.float32)
input_data = input_data.swapaxes(1,2)
input_data = input_data.swapaxes(2,3)
interpreter.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], input_data )
# 解譯器進行推理
interpreter_time_start = time.time()
interpreter.invoke()
interpreter_time_end = time.time()
if args.time =="True" or args.time == "1" :
print( APP_NAME + " Inference Time = ", (interpreter_time_end - interpreter_time_start)*1000 , " ms" )
# 取得解譯器的預測結果
y = []
for output in output_details:
x = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[0]['index'])
#print(x)
if (input_details[0]['dtype']==np.uint8) :
scale, zero_point = output_details[0]['quantization']
x = (x.astype(np.float32) - zero_point) * scale # re-scale
y.append(x)
#print(y[0])
y = [x if isinstance(x, np.ndarray) else x.numpy() for x in y]
y[0][..., :4] *= [width, height, width, height]
# 正規化
pred = non_max_suppression(torch.from_numpy(y[0]), 0.2, 0.4, None, False, max_det=1000)
pred[0] = pred[0][(pred[0][:, 0] - pred[0][:, 2]).abs() >= 10] # H-Filter
pred[0] = pred[0][(pred[0][:, 1] - pred[0][:, 3]).abs() >= 10] # W-Filter
print(pred)
# 建立輸出結果
for idx, det in enumerate(pred):
annotator = Annotator(frame, line_width=3)
if len(det):
det[:, :4] = scale_boxes([width, height], det[:, :4], frame.shape).round()
# Add bbox to image
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
c = int(cls) # integer class
label = Label_name(c)
annotator.box_label(xyxy, label, color=colors(c, True))
# update show-out
frame = annotator.result()
current_time = time.time()
fps = 1 / (current_time - last_frame_time)
last_frame_time = current_time
# 显示FPS
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
cv2.putText(frame, f'FPS: {int(fps)}', (10, 30), font, 1, (0, 255, 0), 2, cv2.LINE_AA)
# 顯示輸出結果
if args.save == "True" or args.save == "1" :
cv2.imwrite( "output/" + APP_NAME + "-" + args.test_img.split("/")[-1][:-4] +'_result.jpg', frame.astype("uint8"))
print("Save Reuslt Image Success , " + APP_NAME + args.test_img.split("/")[-1][:-4] + '_result.jpg')
if args.display =="True" or args.display == "1" :
cv2.imshow('frame', frame.astype('uint8'))
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): break
if (args.display =="False" or args.display == "0") and( args.camera =="False" or args.camera == "0" ) : sys.exit()
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()- Run the application
python3 app.py -c 0 -d 1 --save 0-c 0 means using images as input, -c 1 means using a camera.
-d 1 means turning on result display.
–save 0 means not saving result images.
Note: If you want to change the input source to a camera, change the code from -c 0 to -c 1 (and make sure the device address is correct)。
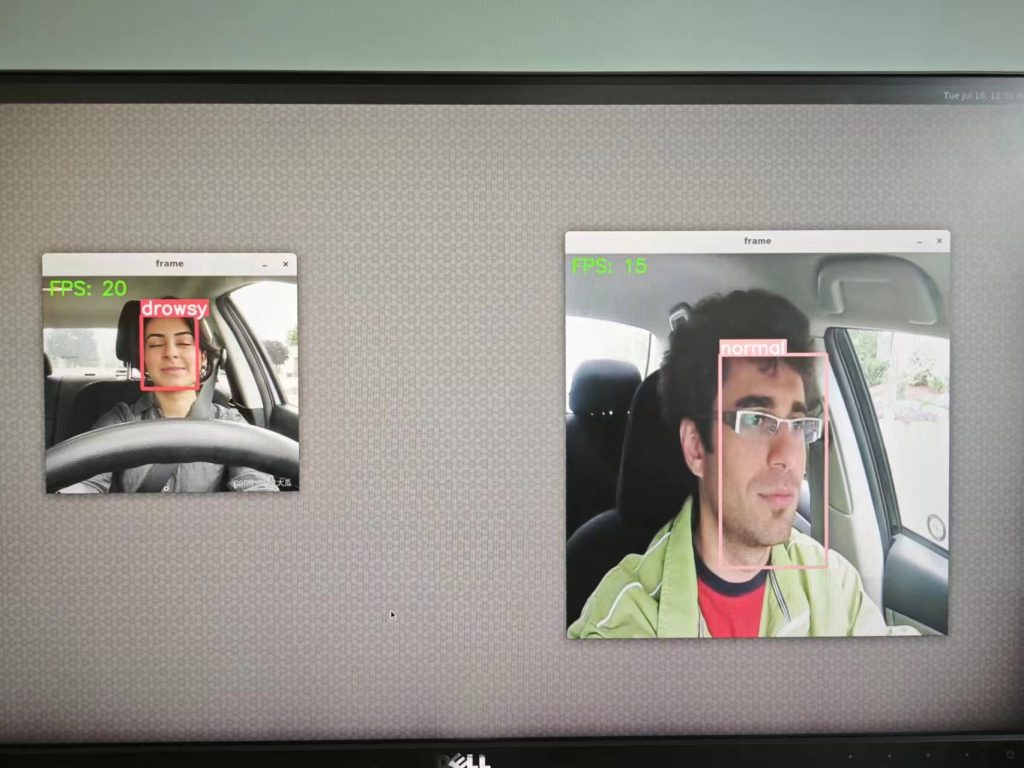
Conclusion
In recent years, countless scholars, researchers and industry players have devoted themselves to studying applications related to object detection. Now, a simple “YOLOv5 object recognition” can be completed in just a few steps, and the model can be trained in just a few hours, which is a world of difference from the past. How to deploy to various hardware platforms is “one of the key indicators of landing”. This article uses “K1” as a device to realize edge computing, and uses the so-called NPU to realize the accelerated computing of the module. It only takes 22 milliseconds (ms) to complete an object recognition! And with the technology of image streaming, it can easily achieve Realtime performance! Let the edge device grasp and respond to the actual situation in the most real time.
References
- i.MX 8 Series Applications Processors Multicore ARM Cortex Processors
- NXP Document – i.MX Yocto Project User’s Guide.pdf
- Welcome to the Yocto Project Documentation
- NXP Document – i.MX Linux Release Note
- NXP Document – i.MX Machine Learning User’s Guide
- Roboflow
- Ultralytics
- https://github.com/tangsanli5201/DeepPCB.git

